Antibiotic prophylaxis in VUR
| Article DOI | https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-92847-3 |
| Objective | To predict which patients with vesicoureteral reflux are most likely to benefit from continuous antibiotic prophylaxis |
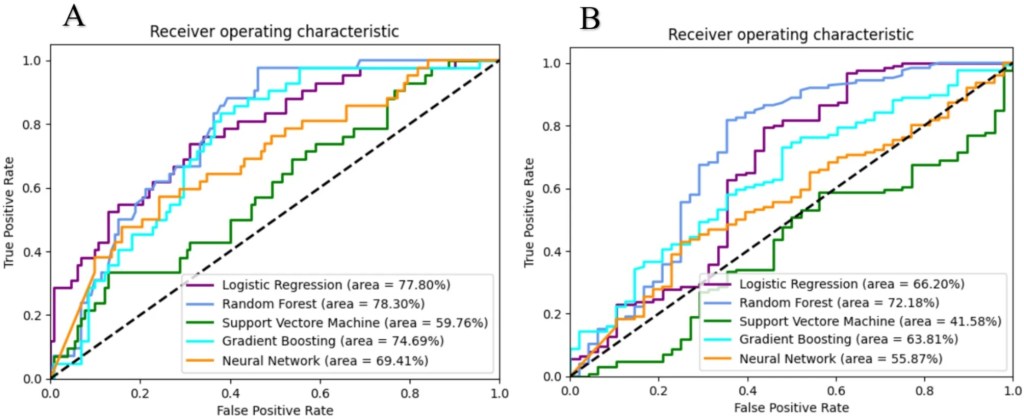
| AI Approach | Logistic regression, random forest, SVM, gradient boosting, CNN |
| Data Source(s) | Two-centre institutional series (225 patients) |
| Model Input | Gender, age at diagnosis, uni- or bilaterality of VUR, DMSA differential renal function, VUR grade, dilating or non-dilating reflux in ultrasonography, presence of fUTI, prenatal hydronephrosis, ureteral anomaly, bladder dysfunction, failure to thrive, renal scarring |
| Model Outcome | Febrile UTI or renal scarring VUR persistence |
| Model Metrics | Predict fUTI and/or renal scarring: AUC 0.78, accuracy 75%, sensitivity 0.64 Predict VUR persistence: Random forest: AUC 0.72, accuracy 72%, sensitivity 0.70 |
| Model Usability | No available code or dataset, no accessible predictive tool. |
AI = Artificial intelligence, VUR = Vesicoureteral Reflux, CNN = Convolutional Neural Network, SVM = Support Vector Machines



Leave a comment