SIRS after PCNL
| Article DOI | https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S518631 |
| Objective | To predict systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) in pediatric patients undergoing percutaneous nephrolithotripsy |
| AI Approach | Random forest, XGBoost, Logistic regression, K-nearest neighbours, Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM), decision tree, SVM, naive bayes (NB) |
| Data Source(s) | Single institutional series (463 patients) |
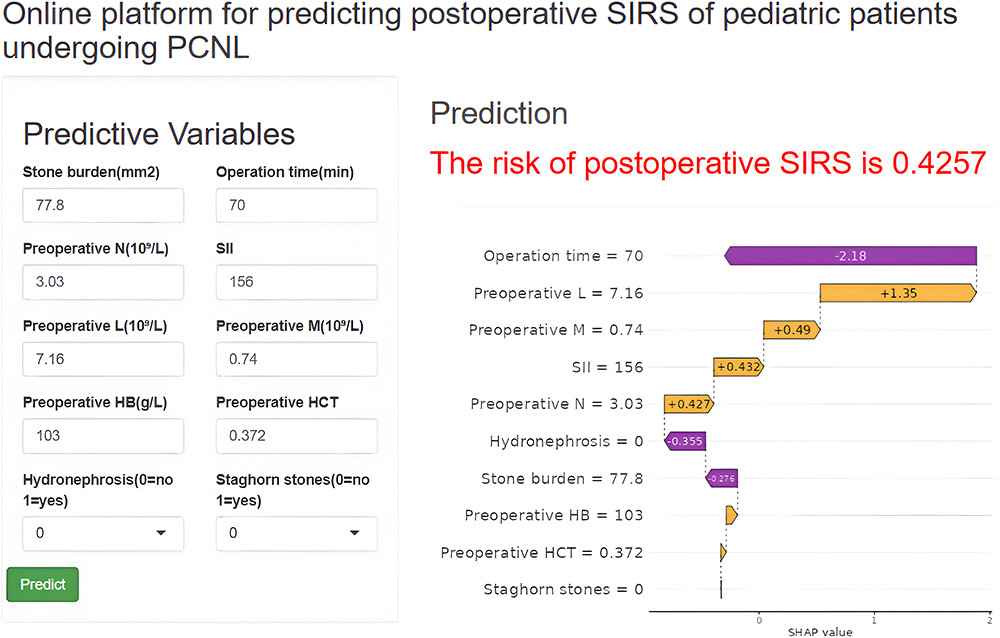
| Model Input | Operation time, stone burden, staghorn stones, hydronephrosis, hemoglobin, hematocrit, neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and SII |
| Model Outcome | SIRS after PCNL |
| Model Metrics | accuracy 0.85, F1 0.65, AUC 0.87, specificity 0.898, sensitivity 0.68 |
| Model Usability | A web-based prediction platform developed using the LightGBM algorithm (https://sirspredict.shinyapps.io/lightgbm/). |
AI = Artificial intelligence, AUC = Area under the receiver operator characteristic



Leave a comment