Chemotherapy myelosupression, Oncology.
| Article DOI | https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041078 |
| Objective | To predict the risk of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression (CIM) in children with Wilms’ tumor. |
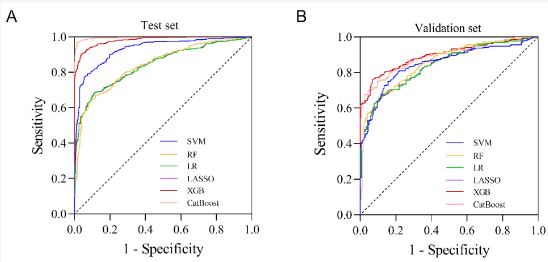
| AI Approach | Extreme Gradient Boosting, Logistic regression, Random Forrest, Lasso, Support Vector Machines, CatBoost |
| Data Source(s) | Single institutional series (437 children, 1433 chemotherapy cycles) |
| Model Input | Age, gender, height, weight, tumor stage, COG grade, the routine hematologic index and biochemical index, routine urinalysis, the type of chemotherapy drugs used, chemotherapy cycles |
| Model Outcome | Grade 2+ chemotherapy induced myelosuppression |
| Model Metrics | AUC of 0.98 in the training set, AUC of 0.90 in the test set, sensitivity 76%, specificity 93%. |
| Model Usability | NA |
AI = Artificial intelligence, AUC = Area under the receiver operator characteristics



Leave a comment